Ophthalmology services in ERRH were available from 1995 however, the first ophthalmologist to join ERRH was Dr. Ngawang Tenzin in 1996.
Since then it started providing primary eye care services for Mongar district and started functioning as a referral center for the health centers in the eastern region of Bhutan. Bhutan provides free basic health care services to citizens. Blindness and visual impairment remain public health challenges globally. Avoidable blindness can be prevented by simple and inexpensive surgery for cataracts and a pair of spectacles for refractive errors.
HOSPITAL BASED OPHTHALMIC SERVICE
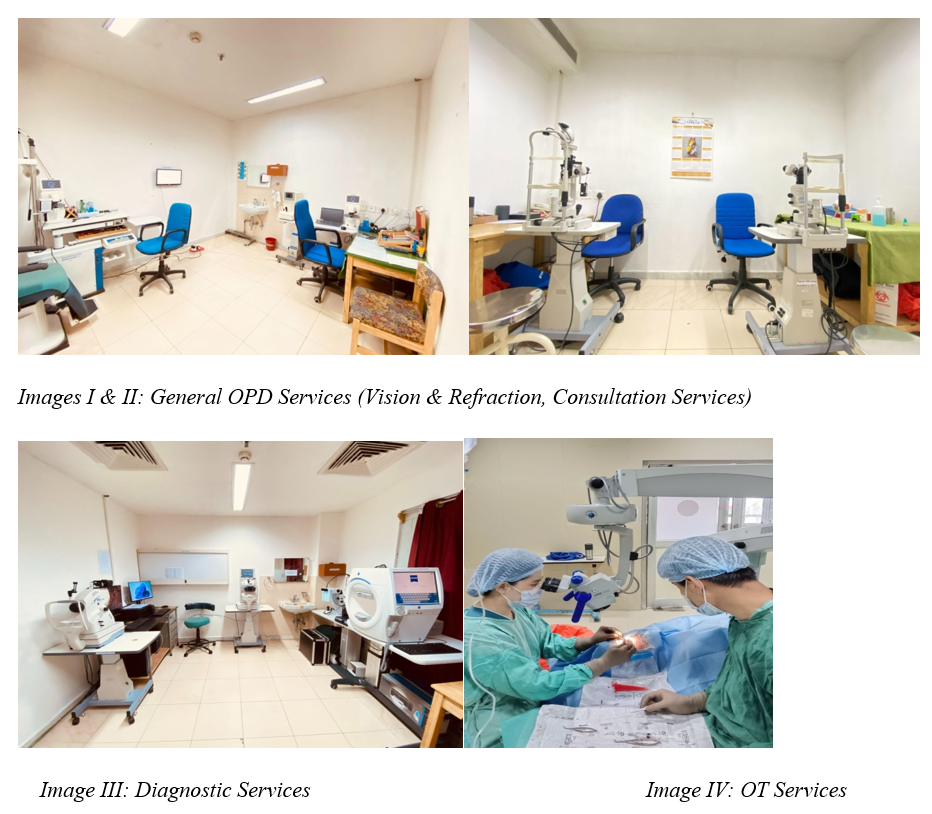
Hospital based ophthalmic services included OPD services, OT services, IPD services and diagnostic services. There are six beds available for the inpatient section in the ward and the beds are shared with the Pediatric ward. Some cases that require further management by sub-specialists are referred to the tertiary center Gyalyum Kesang Choden Wangchuck National Eye Centre, JDWNRH, Thimphu.
Ophthalmic services available at ERRH;
- Vision and Refraction: Visual acuity assessment and refraction both objective and subjective including prescription of glasses.
- Major OT services: Cataract surgery, Pterygium surgery, PI for glaucoma, other major ocular surgery
- Minor OT services: Dressing, suturing, minor procedures like chalazion removal and sac syringing.
- Diagnostic services: OCT, Fundus photo, HVFA, A-B scan, CCT, Keratometry, IOP and ROP screening.
- Orthoptic services: Basic orthoptic test like CT, PBCT, WFDT, Stereopsis test and color vision.
- Contact Lens services: Prescription of CL and counseling on CL wear and care regimen.
- Consultation: Patients are seen by an ophthalmologist.

CHALLENGES
- Limited resource
- Medical equipment like a neodymium YAG laser.
- Preventive education
- There is often a lack of awareness regarding preventive measures for eye diseases. Educating communities about the importance of eye health and preventive care is crucial, but it can be challenging to implement effective awareness programs.
- Access to Eye care services
- Easy access to the eye care services is difficult especially in Eastern Bhutan because of reasons such as geographical area, lack of transportation and insufficient awareness about eye health.
WAY FORWARD
- The way forward for us involves addressing existing challenges, improving services and adapting to changes in healthcare.
- Addressing these above challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving government support, community engagement, international collaborations, and ongoing investment in infrastructure, technology and personal training.
